

The L5 vertebrae rests on the sacrum, a large bone made up of several smaller vertebrae-like bones which have fused together. The foramina are openings for the nerve roots to pass out of the spinal canal and for blood vessels to pass into the canal.
The vertebrae, discs, and ligaments are able to maintain the correct alignment and consequently protect the spinal cord against all but the most violent injury.īetween each adjoining vertebrae on each side of the spinal canal are openings called foramina. Although the ligaments will stretch to permit limited movement, they are rigid enough to maintain alignment of the spinal canal as it passes through each vertebrae. Strong ligaments bind the vertebrae together. Between vertebral bodies are small fibrocartilage cushions called discs.

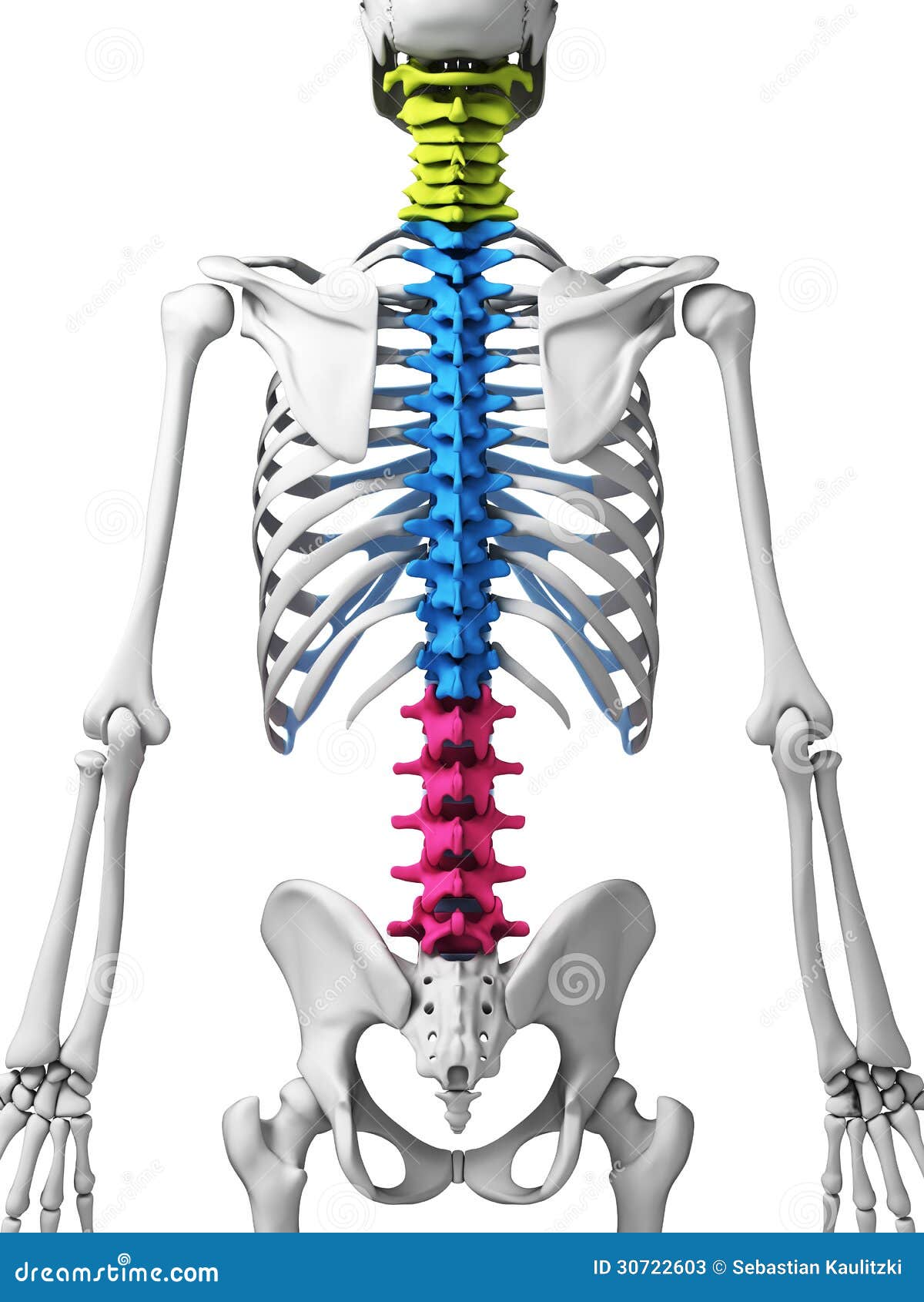
Together with the spinal muscles, these give the back its strength.The manner in which the vertebrae are stacked is shown here. The vertebrae are also held together by tough bands called ligaments. When a disc is damaged (or prolapsed) it is the squidgy liquid in the middle. Each disc is made up of two parts, a tougher fibrous outside and a central substance called nucleus pulposus. They are larger than the cervical vertebrae as they have to support more of the body’s weight. JointsĮach vertebra also has two sets of joints called facet joints which, along with the discs, allows the spine to be flexible allowing us to lead a normal and active lifestyle. Thoracic spine has 12 vertebrae which the ribs attach to. Below this level, the spinal canal contains a group of nerve fibers, called the cauda equina, that go to the pelvis and lower limbs.Ī protective membrane, called the dura mater covers the spinal cord and forms a watertight sac containing spinal fluid. It extends from the brain down to the lower thoracic/ upper lumbar vertebrae. The first cervical vertebra (C1) is called the Atlas. These vertebrae protect the brain stem and the spinal cord, support the skull, and allow for a wide range of head movement. This region consists of seven vertebrae, which are abbreviated C1 through C7 (top to bottom). This is a column of millions of nerve fibres carrying messages from your brain to the rest of your body. The neck region of the spine is known as the Cervical Spine. Each disc has a strong outer ring of fibres called the annulus, and a soft, jelly-like centre called the nucleus pulposus. These are soft pads that act as shock absorbers and prevent the bones from rubbing against each other. The gaps are called foramens, which are covered by the discs at the front and the facet joints at the back. These nerves are called nerve roots and pass through gaps in the arches where they join up to provide sensation and movement to parts of the body. NervesĪ pair of spinal nerves branch out (one to the left and one to the right) from each vertebra. The arches form a hollow tube known as the spinal canal, for the spinal cord to pass through. Behind the body of each vertebra is an arch of bone called the lamina. The front of each vertebra is solid and is called the vertebral body. They protect and support the spinal cord and bear the majority of the weight put upon your spine. Your spine is made up of 24 small bones, called vertebrae that are stacked on top of each other and extend from your skull to your pelvis. The spine is a made up of highly sensitive nerves, flexible ligaments, large muscles and strong bones. The lower back bears a great deal of the weight of the body and for that reason is particularly vulnerable to back pain. The lumbar is located below the thoracic section of the spine. The 'lower back' consisting of 5 vertebrae and the sacrum. This part of the spine has more limited movement so the spinal column is narrower and discs are smaller and thinner. Located below the cervical spine, this area connects to your ribs. The middle section of the back, made up of 12 vertebrae. Two unique vertebrae, the atlas and the axis, are specially adapted to enable such rotation. It is the most flexible and mobile part of the spine, enabling you to move your head freely from side to side and up and down. The neck region containing the top seven spinal vertebrae. The spinal column has three main sections that join together to form an S-like curve when viewed sideways Cervical spine Without a spinal cord you could not move any part of your body, and your organs could not function. The spine is also protects your spinal cord - the column of nerves that connects your brain to the rest of your body, allowing you to control your movements. It allows you to move about freely and to bend with flexibility. Without it you could not stand up or keep yourself upright. The spine gives your body structure and support. Your spine provides both incredible strength and extreme flexibility on many levels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
